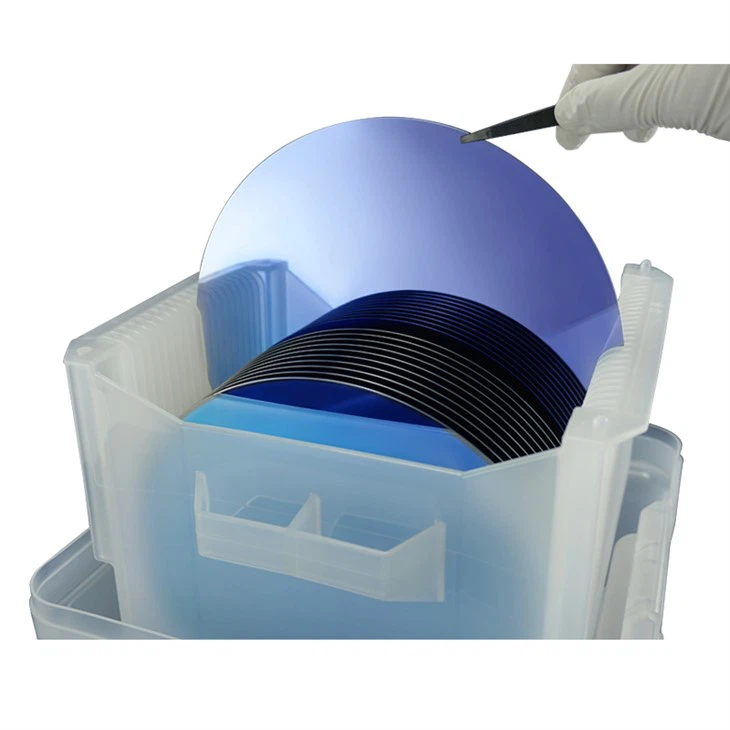
Ningbo Sibranch Microelectronics Technology Co.,Ltd.:Your Trustworthy Thermal Oxide Silicon Wafer Manufacturer!
Founded in 2006 by material science and engineering scientist in Ningbo, China, Sibranch Microelectronics aims to provide semiconductor wafer and service all over the world. Our main products including standard silicon wafers SSP (single side polished), DSP (Double side polished), test silicon wafers and prime silicon wafers, SOI (Silicon on Insulator) wafer and coinroll wafers with diameter up to 12 inch, CZ/MCZ/FZ/NTD, almost any orientation, off cut, high and low resistivity, ultra flat, ultra thin, thick wafers etc.
Leading Service
We are committed to constantly innovating our products to provide foreign customers with a large number of high-quality products to exceed customer satisfaction. We can also provide customized services according to customers' requirements such as size,color,appearance,etc.We can provide the most favorable price and high-quality products.
Quality Guaranteed
We have been continuously researching and innovating to meet the needs of different customers. At the same time, we always adhere to strict quality control to ensure that the quality of every product meets international standards.
Wide Sales Countries
We focus on sales in overseas markets. Our products are exported to Europe, America,Southeast Asia,the Middle East and other regions, and are well received by customers around the world.
Various Types of Products
Our company offers customized silicon wafer processing services tailored to meet the specific needs of our clients. These include Si Wafer BackGrinding,Dicing,DownSizing,Edge Grinding, as well as MEMS among others. We strive to deliver bespoke solutions that exceed expectations and ensure customer satisfaction.
CZ Silicon Wafer are cut from single crystal silicon ingots pulled using the Czochralski CZ growth method, which is most widely used in the electronics industry to grow silicon crystals from large cylindrical silicon ingots used to manufacture semiconductor devices. In this process, an elongated crystalline silicon seed with precise orientation tolerance is introduced into a silicon molten pool with precisely controlled temperature. The seed crystal is slowly pulled upward from the melt at a strictly controlled rate, and crystal solidification of the liquid phase atoms occurs at the interface. During this pulling process, the seed crystal and the crucible rotate in opposite directions, forming a large single crystal silicon with a perfect crystal structure of the seed.
Silicon oxide wafer is an advanced and essential material used in various high-tech industries and applications. It is a high-purity crystalline substance produced by processing high-quality silicon materials, making it an ideal substrate for many different types of electronic and photonic applications.
Dummy wafers (also called as test wafers) are wafers mainly used for experiment and test and being different from general wafers for product. Accordingly, reclaimed wafers are mostly applied as dummy wafers (test wafers).
Gold-coated silicon wafers, and gold-coated silicon chips are used extensively as substrates for analytical characterization of materials. For example, materials deposited onto gold-coated wafers can be analized via ellipsometry, Raman spectroscopy or infrared (IR) spectroscopy due to the high-reflectivity and favorable optical properties of gold.
Silicon Epitaxial Wafers are highly versatile and can be manufactured in a range of sizes and thicknesses to suit different industry requirements. They are also used in a variety of applications, including integrated circuits, microprocessors, sensors, power electronics, and photovoltaics.
Manufactured using the latest technology and is designed to offer unparalleled reliability and consistency in performance. Thermal Oxide Dry and Wet is an essential tool for semiconductor manufacturers worldwide as it provides an efficient way to produce high-quality wafers that meet all the demanding requirements of the industry.
What are ultra-thin silicon wafers? Wafers with a thickness of 200 micron of thinner use the following for their thinning process mechanical grinding, stress reduction, polishing and etching. Presently and in the future ultra-thin silicon are important building blocks for the manufacture of semiconductor devices.
This wafer has a diameter of 300 millimeters, making it larger than traditional wafer sizes. This larger size makes it more cost-effective and efficient, allowing for greater production output without sacrificing quality.
The 100mm silicon wafer is a high-quality product that is widely used in the electronics and semiconductor industries. This wafer is designed to provide optimal performance, precision, and reliability that are essential in the manufacturing of semiconductor devices.
What is Thermal Oxide Silicon Wafer
Thermal Oxide Silicon Wafer are silicon wafers that have a layer of silicon dioxide (SiO2) formed on them. Thermal oxide (Si+SiO2) or silicon dioxide layer is formed on a bare silicon wafer surface at elevated temperature in an oxidant's presence through the thermal oxidation process. It is usually grown in a horizontal tube furnace with a temperature range from 900°C ~ 1200°C, using either a "Wet" or "Dry" growth method. Thermal oxide is a kind of "grown" oxide layer. Compared to the CVD deposited oxide layer, it is an excellent dielectric layer as an insulator with higher uniformity and higher dielectric strength. For most silicon-based devices, the thermal oxide layer is a significant material for pacifying the silicon surface to act as doping barriers and surface dielectrics.
Types Of Thermal Oxide Silicon Wafer
Wet Thermal Oxide On Both Sides Of Wafer
Film thickness: 500Å – 10µm on both sides
Film thickness Tolerance: Target ±5%
Film stress: – 320±50 MPa Compressive
Wet Thermal Oxide On Single Side Of Wafer
Film thickness: 500Å – 10,000Å on both sides
Film thickness Tolerance: Target ±5%
Film stress: -320±50 MPa Compressive
Dry Thermal Oxide On Both Sides Of Wafer
Film thickness: 100Å – 3,000Å on both sides
Film thickness Tolerance: Target ±5%
Film stress: – 320±50 MPa Compressive
Dry Thermal Oxide On Single Side Of Wafer
Film thickness: 100Å – 3,000Å on both sides
Film thickness Tolerance: Target ±5%
Film stress: – 320±50 MPa Compressive
Dry Chlorinated Thermal Oxide With Forming Gas Anneal
Film thickness: 100Å – 3,000Å on both sides
Film thickness Tolerance: Target ±5%
Film stress: – 320±50 MPa Compressive
Sides Process: Both Sides
The thermal oxidation of silicon begins by placing the silicon wafers in a quartz rack, commonly known as a boat, which is heated in a quartz thermal oxidation furnace. The temperature in the furnace may be between 950 and 1,250 degrees Celsius under standard pressure. A control system is needed to keep the wafers within about 19 degrees Celsius of the desired temperature.
Oxygen or steam is introduced into the thermal oxidation furnace, depending on the type of oxidation being performed.
Oxygen from these gases then diffuses from the surface of the substrate through the oxide layer to the silicon layer. The composition and depth of the oxidation layer may be precisely controlled by parameters such as time, temperature, pressure and gas concentration.
A high temperature increases the oxidation rate, but it also increases the impurities and movement of the junction between the silicon and oxide layers.
These characteristics are particularly undesirable when the oxidation process requires multiple steps, as is the case with complex ICs. A lower temperature produces an oxide layer of higher quality, but also increases the growth time.
The typical solution to this problem is to heat the wafers at a relatively low temperature and high pressure to reduce the growth time.
An increase of one standard atmosphere (atm) decreases the required temperature by about 20 degrees Celsius, assuming all other factors are equal. Industrial applications of thermal oxidation use up to 25 atm of pressure with a temperature between 700 and 900 degrees Celsius.
The oxide growth rate is initially very fast but slows down as oxygen must diffuse through a thicker oxide layer to reach the silicon substrate. Almost 46 percent of the oxide layer penetrates the original substrate after oxidation is complete, leaving 54 percent of the oxide layer on top of the substrate.
FAQ
Why Choose Us
Our products are sourced exclusively from the world's top five manufacturers and leading domestic factories. Supported by highly skilled domestic and international technical teams and stringent quality control measures.
Our objective is to provide customers with comprehensive one-on-one support, ensuring smooth channels of communication that are professional, timely, and efficient. We offer a low minimum order quantity and guarantee swift delivery within 24 hours.
Factory Show
Our vast inventory consists of 1000+ products, ensuring that customers can place orders for as little as one piece. Our self-owned equipments for dicing & backgrinding, and full cooperation in the global industrial chain enable us prompt shipment to ensure customer one-stop satisfaction and convenience.



Our Certificate
Our company takes pride in the various certifications we have earned, including our patent certificate, ISO9001 certificate, and National High-Tech Enterprise certificate. These certifications represent our dedication to innovation, quality management, and commitment to excellence.
Hot Tags: thermal oxide silicon wafer, China thermal oxide silicon wafer manufacturers, suppliers, factory, epitaxial silicon wafer, float zone silicon wafer, 12 inch silicon wafers, thick silicon wafers, 12 Inch Silicon Wafer, 450 mm silicon wafer